Homeopathy & Acne
 Acne is a chronic inflammation of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, characterized by an eruption which is hard, conical in shape, of moderate size and with redness. It commonly occurs in puberty & in the spring season.
Acne is a chronic inflammation of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, characterized by an eruption which is hard, conical in shape, of moderate size and with redness. It commonly occurs in puberty & in the spring season.Types: -
The disease appears in its different varieties and the well known forms are-
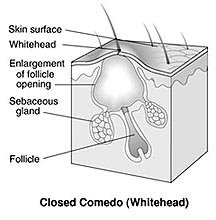
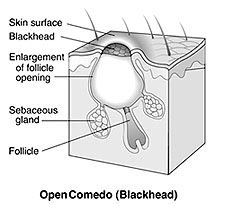
1 Acne simplex or vulgaris- This type of acne is common in youth, appearing from 12th to 18th year and lasting from 5 to 10 years if untreated. It is most often seen on the face, especially on the forehead, cheeks and chin, but is quite common on the upper part of the shoulders and chest and may rarely be found elsewhere. The eruptions are bilateral without symmetry and consist of comedones, papules and pustules from pin-head to split pea in size, varying in number from one or two to hundreds.
2 Acne indurate- It is more common in the back and neck. It is chronic in its course, which rarely disappears without treatment. The lesion appears as deep seated, round, ovoid or flattish indurations or nodules. They may be few or many, isolated or aggregated, vary in size from a pea to a cherry, and as they enlarge, the covering skin becomes dark red in color. Most are indolent or blind boil, which contain little pus and even if incised are apt to reform. Nearby glands may be affected.
 3 Acne Rosacea- It is a chronic congestion of the face which appears between the thirtieth and fortieth years of life. Women up to the age of forty seem more subjected to the disease than men. It begins with temporary hyperemia which is characterized by flushing, permanent redness, capillary dilatation, secondary acne and sometimes by tissue hypertrophy. The rosacea begins as a temporary congestion or redness of the middle third i.e. flush area of the face, which recurs at varying intervals.
3 Acne Rosacea- It is a chronic congestion of the face which appears between the thirtieth and fortieth years of life. Women up to the age of forty seem more subjected to the disease than men. It begins with temporary hyperemia which is characterized by flushing, permanent redness, capillary dilatation, secondary acne and sometimes by tissue hypertrophy. The rosacea begins as a temporary congestion or redness of the middle third i.e. flush area of the face, which recurs at varying intervals.4 Acne Varioliformis- It is a rare, chronic inflammatory disease, characterized by papulopustules commonly occurs in the forehead and scalp, occasionally in the other locations, and leaving a depressed scar similar to that of variola. The initial lesions are small pale macules or papules which soon become reddish-brown, deep-seated, indolent papules, pea to bean-sized and frequently pierced by a hair. Later vesicles and pustules develop, covered with flat, adherent, yellowish brown crusts under which will be found sharply defined, rounded ulcers. These crusts may increase in size but eventually fall off, leaving reddish brown, clear-cut, variola like scars which finally becomes white.
5 Acne Punctata- In acne punctat, there is an irritative process around a hair follicle by the collection of sebaceous matter, in the form of pointed eruption. This collection, when squeezed out of the skin, is emitted in a cylindrical form, having the appearance of a small comedo. This variety is generally seen in persons at the age of puberty who take little exercise and indulge in eating excess fat and carbohydrates. It is most frequent in young females.
 Aetiology:
Aetiology: The following factors are possibly responsible.
a). Androgenic influence: In many young females excess androgen is seen even after the teen where the disease is very much prevalent.
b). Excessive sebaceous secretion: Due to influence of the androgenic hormones there is excessive secretion of sebaceous glands which play a basic role.
c). Abnormal keratinisation: The follicular duct undergoes keratinisation which is an early finding in acne.
d). Infection: An anaerobic diphtheroid known as propionibacterium Acnes having lipolytic activity is seen within the pilosebaceous ducts. They also alter the cell mediated immunity.
Treatment:
1 The face should be washed with soap and water about 4-5 times a day so that the greasy materials are washed off.
2 Manual removals of the comedones may be advised.
3 Zinc sulphide lotions B.P.C. may be applied locally.
4 Mild peeling agents containing Benzoic Peroxide (2.5-10%) in combination with sulphur in ointment or gel may be used.
5 Contraceptive pills containing less androgenic effect of Progesterone may also be beneficial.
6 Good food, fresh air and sun light are also beneficial.
7 Antibiotics like tetracycline, erythromycin, oxytetracycline or cotrimoxazole may be taken orally.
8 Topical antibiotics like 1% Clindamycin in alcohol may also be helpful.
Homeopathic Treatment:
1. Antim crude. Small red pimple on the face; Acne of drunkards with gastric derangements, thirst and white coated tongue.
2. Antim tart. Obstinate cases, with tendency to postulation, are curable with this remedy.
3. Arsenic alb. Acne with burning sensation.
4. Arsenicum Sulph Rubrum. Is indicated in acne accompanied by eczema or psoriasis.
5. Asterias Rubens. Is the head remedy for pimples on the face at the age of puberty.
6. Aurum Arsenicum. Acne, pimple on the face and forehead, pustules.
7. Belladonna. For acne which is very painful and red in color; occurs in plethoric persons.
8. Berberis Aquifolium. For acne on the face especially in girls where the skin becomes rough. Along with internal medication its mother tincture should be used for local application on acne for best results.
9. Bovista. Acne which occurs due to cosmetics, especially during summer.
10. Calc carb. Acne due to menstrual disorder with excessive perspiration.
11. Calc Phos. Acne in anaemic girls at puberty, with vertex headache and flatulent dyspepsia, relieved by eating.
12. Calc Sulph. Being the chief blood purifier it proves an indispensable remedy in all stages of the affection. It is especially indicated where the pimples suppurate.
13. Carboveg. Acne due to gastric derangement.
14. Dulcamara. Rash on the face before menses.
15. Hepar Sulph. Pimples of the size of a pea in different parts of the body, the slightest scratch or injury inclines to ulceration.
16. Kali bromatum. This remedy is especially adapted to the acne simplex and the indurate, especially in hyperaesthetic, nervous females, and in epileptics who have been maltreated by bromides.
17. Streptococcin. Acne, which is aggravated by taking eggs and during winter.
18. Other medicines used in acne are: Thuja, Sulphur, Silicea, Sepia, Sanguinaria can, Rhus tox, Pulsatilla, Psorinum, Petroleum, Nitric acid, Nat mur, Mercurius, Ledum, Lachesis, Hydrocotyle, Causticum, Calc picrata, Borax, Agaricus, Alumina, Arsenic Iodatum, etc.


3 Comments:
It would be nice to find a post from you explaining what is homeopathy explained in lay man`s terms.
Thanks for the through coverage of information.
Gilberto
Hello,
This is a very informative blog and came across it as I was searching for hirsuitism treatments. Can I get info from you regd a homeo doctor who could help me out at Bangalore? Is there an email id I can write to you to communicate?My email id is shri_mb@hotmail.com
Thank you very much.
Shri
For milder cases of acne there are over the counter treatments and other skin care solutions that contain benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid. There are also a variety of on-line ordered products that are very effective, like proactiv acne medicine. Remember, pregnant women should avoid products that contain salicylic acid, as it can possibly lead to complications during pregnancy or even birth defects. These are to be applied normally after washing, just like with facial acne solutions.
Post a Comment
<< Home